Quantum sensors—masters of precision, exist in a number of states concurrently utilizing superposition and entanglement, guided by laser mild for meticulous management.
They’re now discovering wide-ranging purposes.
In plant physiology and horticulture, mild is pivotal for plant progress. Nonetheless, not all mild is equal in its impression on plant photosynthesis and well being. Photosynthetically energetic radiation (PAR), the 400 to 700 nanometre mild wavelength vary, is essential for photosynthesis.
PAR quantum sensors, utilizing superior photodiode know-how, precisely measure PAR depth. They utilise superior photodiode know-how that may precisely detect and measure the variety of photons inside the PAR vary. Outfitted with a light-sensitive photodiode, sign amplifier, and digital interface, these sensors present exact measurements of sunshine vitality for optimum plant cultivation and greenhouse administration. By understanding the PAR ranges in numerous progress environments, researchers can optimise plant cultivation methods, improve crop yields, and examine the results of sunshine on numerous plant species.
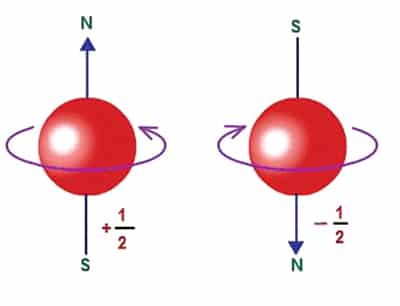 Two spin natures of the electron, principally optimistic and destructive spin half
Two spin natures of the electron, principally optimistic and destructive spin half
PAR quantum sensors provide a number of benefits over conventional mild meters. First, they’re particularly calibrated to measure mild inside the PAR vary, guaranteeing correct readings for photosynthetic exercise. Second, these sensors are sometimes compact and moveable, permitting for straightforward deployment and information assortment in numerous settings. Many PAR sensors additionally provide real-time monitoring capabilities, enabling researchers to trace fluctuations in mild depth over time.
The information collected by PAR quantum sensors can be utilized to calculate necessary parameters, comparable to photosynthetic photon flux density (PPFD), which quantifies the variety of photons reaching a selected space per unit time. PPFD is a essential metric for figuring out mild necessities, optimising lighting programs, and understanding plant responses to completely different mild circumstances.
Working
Quantum sensors use quantum mechanics rules for exact measurements. The working precept of quantum sensors includes a number of key ideas and methods.
One necessary idea in quantum sensing is superposition. In response to quantum mechanics, particles can exist in a number of states concurrently. Within the case of quantum sensors, which means that the sensor may be in a superposition of various states, every equivalent to a distinct worth of the measured amount. By manipulating and measuring the superposition state, quantum sensors can receive exact details about the bodily parameter being measured.
One other essential idea is entanglement. Entanglement happens when two or extra particles change into correlated in such a manner that the state of 1 particle is instantly linked to the state of the others, whatever the distance between them.
Quantum sensors can reap the benefits of entanglement to reinforce their measurement capabilities. For example, by entangling two particles and measuring considered one of them, it’s doable to realize details about the opposite particle with out instantly measuring it. This allows quantum sensors to beat sure limitations of classical sensors and obtain larger sensitivity.
Quantum sensors make use of numerous methods to control and measure quantum states. One frequent method is utilizing laser mild to work together with the quantum system. Laser mild interplay with the quantum system permits for exact management and measurement of the sensor’s properties. By fastidiously controlling the laser’s properties, comparable to frequency and depth, scientists can manipulate the superposition and entanglement states of the sensor.
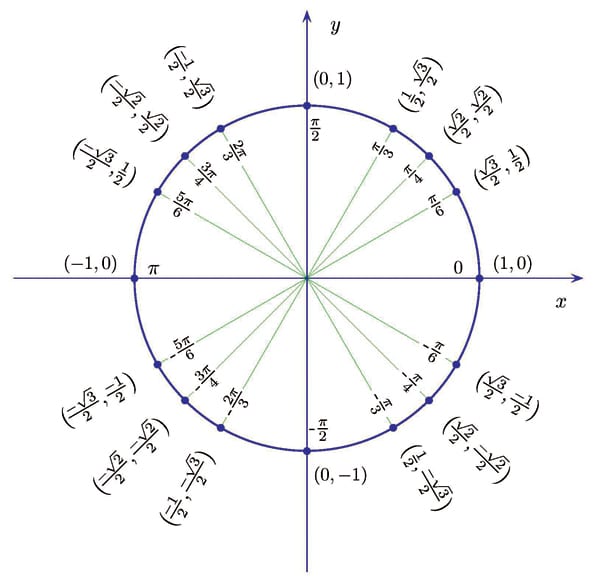 The state of the system the place every qubit is represented within the q sphere related to the computation is represented within the level on the floor of the sphere
The state of the system the place every qubit is represented within the q sphere related to the computation is represented within the level on the floor of the sphere
Purposes
1. Quantum metrology. Revolutionising metrology, quantum sensors allow ultra-precise measurements in atomic clocks, which is important for world navigation programs like GPS. These clocks exploit the frequency stability of quantum transitions to offer correct timekeeping.
2. Gravitational wave detection. Quantum sensors play an important function in detecting gravitational waves, that are ripples within the cloth of spacetime. Gadgets like interferometers, which measure minuscule modifications within the lengths of two arms, use quantum-enhanced methods to extend their sensitivity, permitting the detection of extremely weak gravitational wave indicators.
3. Magnetic area sensing. Quantum sensors can measure magnetic fields with distinctive precision. They discover purposes in numerous areas, comparable to medical diagnostics, mineral exploration, and environmental monitoring. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines, for instance, utilise quantum sensors to map inside physique buildings.
4. Quantum communication and cryptography. Quantum sensors are integral to quantum communication programs. They permit safe transmission of data by quantum key distribution (QKD), which makes use of the rules of quantum mechanics to make sure unbreakable encryption. Quantum sensors can detect eavesdroppers trying to intercept the transmitted quantum states.
5. Quantum imaging. Quantum sensors allow imaging methods that surpass classical limitations. Quantum-enhanced imaging can present larger decision and sensitivity, making it helpful for biomedical imaging, surveillance, and supplies characterisation. Quantum ghost imaging, as an illustration, reconstructs photos utilizing correlated photon pairs with out instantly interacting with the article being imaged.
6. Gravity and inertial sensing. Quantum sensors can measure tiny modifications in acceleration and gravitational forces. These sensors have purposes in geophysical surveys, inertial navigation programs, and earthquake detection. They will detect slight variations in gravity, enabling the mapping of underground buildings or monitoring volcanic exercise.
7. Quantum chemical sensing. Quantum sensors allow extremely correct and delicate detection of chemical compounds. They discover purposes in environmental monitoring, industrial processes, and medical diagnostics. Quantum sensors can detect hint quantities of pollution, analyse fuel composition, and determine biomarkers in organic samples.
These are only a few examples of the wide-ranging purposes of quantum sensors. As analysis and growth in quantum know-how proceed to advance, we will anticipate additional breakthroughs and the emergence of recent purposes in fields comparable to quantum computing, quantum biology, and extra. Quantum sensors maintain nice promise for remodeling numerous industries and pushing the boundaries of scientific exploration.
Quantum sensors have emerged as highly effective instruments with immense potential throughout a variety of purposes. Leveraging the rules of quantum mechanics, these sensors have revolutionised metrology, enabling ultra-precise measurements in fields comparable to timekeeping, gravitational wave detection, and magnetic area sensing. They’ve paved the best way for developments in quantum communication and cryptography, providing safe transmission of data. Quantum sensors have additionally pushed the boundaries of imaging methods, offering larger decision and sensitivity in biomedical imaging, surveillance, and supplies characterisation.
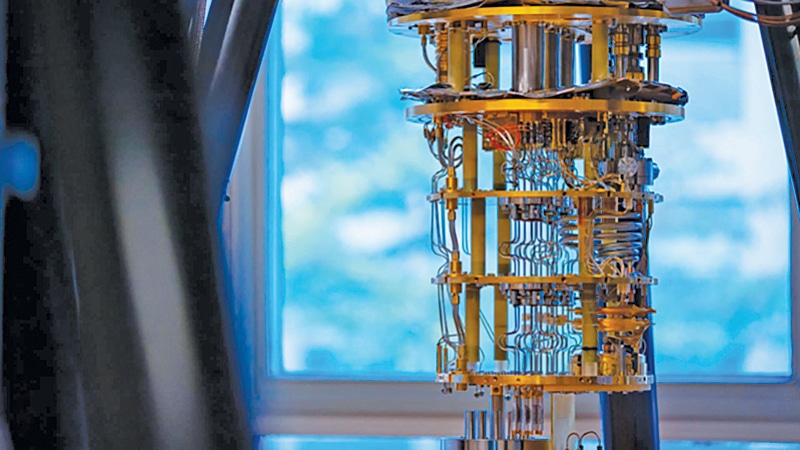 The quantum {hardware} the place it really works spin nature of the electrons (Courtesy: Intel)
The quantum {hardware} the place it really works spin nature of the electrons (Courtesy: Intel)
Moreover, they’ve discovered utility in gravity and inertial sensing, enabling exact measurements of acceleration and gravitational forces for geophysical surveys and navigation programs. Moreover, quantum sensors contribute to the sector of quantum chemistry, facilitating the correct detection and evaluation of chemical compounds. As analysis in quantum know-how progresses, we will anticipate additional breakthroughs and new purposes in numerous fields, driving innovation and shaping the long run. With their exceptional capabilities, quantum sensors maintain the promise of reworking industries, advancing scientific exploration, and opening up new frontiers of information.
The writer, Duraiarasu E, is pursuing B.E ECE at Rajalakshmi Engineering School, Chennai. His areas of curiosity are IoT, VLSI, embedded programs, machine studying, 3D printing, and MEMS
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink






