[ad_1]
Mar 13, 2024
(Nanowerk Information) What precisely occurs on the tiny scale at which particular person atoms exist and work together? SMU chemist Elfi Kraka and her colleagues have been engaged on creating a computational device aimed toward offering solutions to that thriller.
Mathematical capabilities used to calculate the potential vitality of a system of atoms are known as interatomic potentials. Machine studying interatomic potentials (MLIP)s have grow to be an environment friendly and cheaper different to conventional quantum chemical simulations, which even on at this time’s high-performance computing typically grow to be out of attain for bigger programs. Of their quest, the researchers developed a novel MLIP, known as ANI-1xnr that’s relevant to a broad vary of reactive chemistry with out the necessity for expensive refitting, a significant downside of the MLIPs presently in use.
Their findings seem within the journal Nature Chemistry (“Exploring the frontiers of condensed-phase chemistry with a common reactive machine studying potential”).
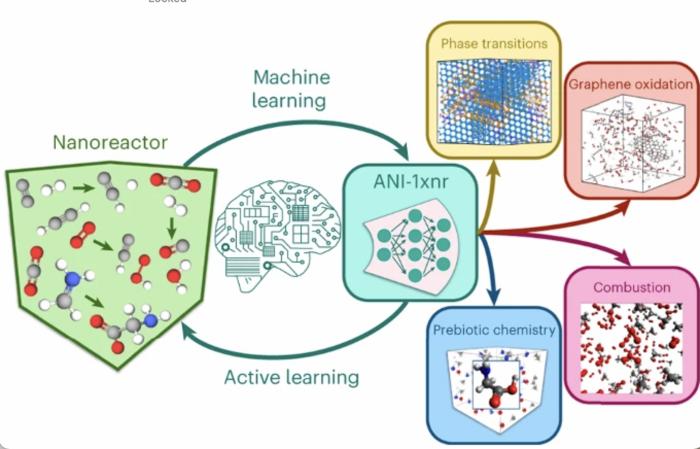
Researchers developed a common reactive MLIP (ANI-1xnr) by means of automated sampling of condensed-phase reactions. ANI-1xnr was then utilized to check 5 distinct programs: carbon solid-phase nucleation, graphene ring formation from acetylene, biofuel components, combustion of methane and the spontaneous formation of glycine from early earth small molecules. (© Nature Chemistry)
“Understanding interactions on the atomic degree might assist us in caring for our planet, influence the methods medicine work together with the human physique, and even allow us to discover natural supplies which have come to Earth due to comets and asteroids or simulate chemical reactions happening far out in area together with star dusts or interstellar grains,” Kraka mentioned.
Kraka and her colleagues put their new ANI-1xnr potential to the check, simulating 5 distinct programs in excessive environments: carbon solid-phase nucleation, graphene ring formation from acetylene, biofuel components, combustion of methane and the spontaneous formation of glycine from early earth small molecules (the well-known Miller experiment), with all 5 carefully matching accessible experimental or theoretical information.
Miller performed an experiment in 1959, making use of electrical energy to a combination of straightforward molecules, corresponding to ammonia, carbon monoxide, water, hydrogen, and methane uncovering how amino acids, essential life-building blocks, have been fashioned. His experiment created a brand new subject of research known as prebiotic chemistry, which goals to grasp the chemical processes and reactions that occurred on Earth earlier than the emergence of life. Since then, scientists have referred to Miller’s experiment to grasp particular reactions that result in the formation of amino acids below Early Earth situations.
The ANI-1xnr dataset is now accessible publicly for analysis use. The authors intend broaden and additional prepare ANI-1xnr over time, the place Kraka is especially serious about exploring the formation of amino acids and precursors of DNA from small molecules below extraterrestrial situations, considered one of her latest analysis pursuits.
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink




