[ad_1]
Google’s Gary Illyes answered a query about canonicalization, indexing and core algorithm updates that provides a clearer image of how the totally different methods work collectively however independently.
A search marketer named David Minchala requested if Google’s canonicalization processes nonetheless labored however in a slower method throughout a core algorithm replace. The reply to that query is fascinating as a result of it affords a option to higher perceive how these backend processes perform.
David’s query used the phrase “posit” which implies to place an concept or assertion ahead for consideration as a doable truth.
That is the query:
“Posit: throughout core algo updates (and perhaps any massive replace?), indexing providers like canonicalization (i.e., choosing the URL to index and merging all alerts from different recognized duplicate URLs) nonetheless work however are slower. Possibly a lot slower.
Any likelihood for a remark, Gary Illyes or John Mueller ? Is also a superb subject for Search Off the File: what are the technical calls for on Google to roll out core updates and the way may that have an effect on “regular” providers like crawling and indexing.”
Google’s Gary Illyes responded by saying that the posited assertion is inaccurate, utilizing an analogy to clarify how the 2 issues perform. Gary particularly mentions the index choice course of (the place Google chooses what goes into the index) and canonicalization (selecting which URL represents the webpage when there are duplicates).
He defined:
“the posit is inaccurate. these methods are impartial from the “core updates”.
consider core updates as taking part in with cooking substances: you alter how a lot salt or msg you set in your stir fry and you may transform the outcome.
on this context index choice and canonicalization is extra about what’s occurring within the salt mines or the msg factories; not a lot to do with the cooking simply but.”
Google Indexing Engine
So in different phrases, what occurs in a core replace occurs independently from the index choice and canonicalization processes. That means of it, as Gary Illyes urged, aligns with lots of Google’s patents that describe how search methods work. When speaking a couple of search engine, patents describe them as a group of engines, utilizing the phrase “indexing engine” when speaking about indexing.
For instance, in a single patent illustration there’s an indexing engine, a rating engine, and a rating modification engine. Knowledge goes out and in of every engine the place it will get processed in response to its perform.
Screenshot From A Google Patent
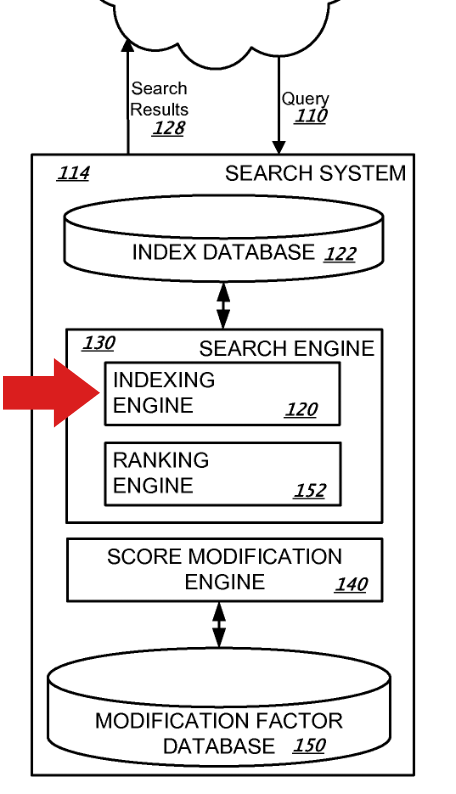 Flowchart depicting a search system. It features a question enter, search outcomes output, elements like an index database, indexing engine, rating engine, and a rating modification database.
Flowchart depicting a search system. It features a question enter, search outcomes output, elements like an index database, indexing engine, rating engine, and a rating modification database.
The above screenshot makes it simpler to know what a search engine is and the way the totally different components work collectively and individually as effectively.
Learn the LinkedIn dialogue right here.
Learn additionally: Google Explains How It Chooses Canonical Webpages
Featured Picture by Shutterstock/Roman Samborskyi
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink

